A customer’s revenue potential doesn’t end at the point of sale. There’s a wealth of opportunity for more business after purchase — and practices such as cross-selling and upselling can help you tap into it.

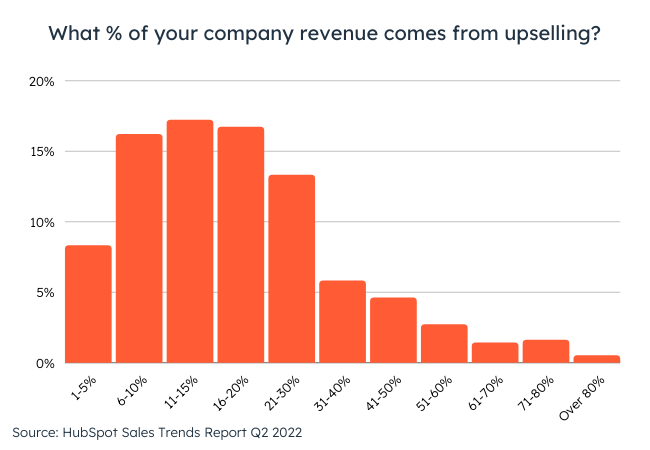
In fact, according to a 2022 HubSpot Blog survey of more than 500 sales professionals, 72% of salespeople who upsell and 74% who cross-sell say that it drives up to 30% of their revenue.
Here, we’ll take a closer look at:
What is cross-selling?
Cross-selling is encouraging the purchase of anything in conjunction with the primary product. For example, if a customer has already purchased a subscription to your marketing tool, cross-selling would encourage that customer to purchase a subscription to your CRM.
If your company offers a separate product or service that can complement or enhance a customer’s initial purchase, cross-selling can be an excellent opportunity to generate extra revenue.
According to HubSpot Research, 67.6% of cross-selling sales professionals offer discounts and promotions, and another 66.1% recommend related or complementary products and services.
Cross-Selling a Cheeseburger
Say you work at a fast-food franchise, and a patron orders a burger. If you wanted to cross-sell, you would offer extra items to make for a complete meal.
For example, you might ask if they want to add an order of fries and a milkshake to go along with the burger. In this case, you’re building around the initial purchase with complementary products.

Cross-Selling Example
Imagine you work for an ed-tech company that sells a suite of automation software to assist university administrators. You offer three products — one for curriculum planning, one for classroom scheduling, and one for academic reporting.
You’ve connected with a college that has agreed to buy your curriculum planning software. If you wanted to cross-sell them, you’d pitch them one or both of your other products and explain how they work together to simplify academic administrative tasks.
In this instance, you wouldn’t be offering an upgraded version of the software the prospect purchased, but separate products that complement one another in the interest of alleviating their pain points.
What is upselling?
Upselling is encouraging the purchase of anything that would make a customer’s additional purchase more expensive with an upgrade, enhancement, or premium option.
With upselling, you’re not offering lateral products to complement your customer’s initial purchase — you’re offering an upgraded or premium version of the product they’ve just agreed to buy.
In short, you’re “piling on” on a product when upselling — not “building around” it.
HubSpot research says that 88% of surveyed salespeople try to upsell their customers. 49% of that group say that understanding customers’ needs and goals is a key strategy.
Upselling a Cheeseburger
Let’s continue with the fast food burger example from above. To upsell a burger, you’d offer options for a more elaborate burger. So, for example, adding a slice of cheese or a pickle for an additional fee. Or, you could tell them about a higher-quality cut of beef they could choose for a small premium.

You might try to get them to add an extra patty or a few strips of bacon for an additional fee — or you could tell them about a higher-quality cut of beef they could choose for a small premium. One way or another, you would take the central item they agreed to buy and sell them on ways to enhance it.
Upselling Example
For a more realistic example, consider a business that sells sales automation software to small-to-medium-sized businesses. The company offers three tiered plans with additional features on more expensive plans.
A rep from the company is currently working out a deal with a small business that’s agreed to purchase the least expensive of the three available options. If the rep wanted to upsell their prospect, they would likely tout the relevant features the middle-tier option offers that the lower-tier option doesn’t.
Let’s say the prospect’s business is maturing, so it will lean more heavily on accurate forecasting. In our scenario, the bottom-tier plan lacks the forecasting resources that the middle-tier option provides.
With that in mind, the rep might try to upsell the prospect by stressing how upgrading to the higher option will ensure that their business is adequately prepared to easily create accurate, productive forecasts as it expands.
What’s the difference between cross-selling and upselling?
The difference between cross-selling and upselling is in their names. Cross-selling adds to a sale through additional, lateral products that complement the initial purchase. Upselling adds to a purchase by selling a prospect an upgraded or enhanced version of the original product.
The terms are often used interchangeably, but the approaches for each are different.

Continuing with the fast food example, you’d upsell by enhancing the burger itself with added toppings, but you’d cross-sell by offering more options in addition and separate to the burger.
With this in mind, let’s go over some techniques for cross-selling that will help you close the deal every time.
How to Cross-Sell and Upsell
Cross-selling and upselling can happen at any point in the buyer’s journey. And HubSpot research says that mapping out the customer journey to identify the most effective opportunities to upsell or cross-sell is one of the most effective strategies. Other top strategies include:
Below are our best practices to learn how to cross-sell and upsell:
1. Get to know your audience.
You may already know about buyer personas, but it’s important to get to know your audience once they’ve already bought your product, too. Use demographic and psychographic information about your customers — along with customer feedback — to create personas for your customers and understand their goals and challenges to identify the most helpful, relevant products you could cross-sell and upsell.
2. Build out customer journeys.
Next, map out customer journeys to identify how they will use your product and how it will help them grow. When your customers get to the point where they’re seeing results (thanks to your product), they’ll start telling other people about it and driving referrals.
At that point in the customer journey, they’ll likely be excited to hear your cross-sell or upsell pitch and spring some extra money for your additional offering.
Wait until they’re ready before trying to cross-sell or upsell. During the post-purchase period — after purchase, during onboarding, and before they’ve seen its value — you’ll have a hard time selling them on additional products or features.
3. Think about problems and offer solutions that map to products.
Before you hop on a call or email and attempt to sell to an existing customer, take some time to review your product offerings and find their current spot on your customer journey.
That way, you’ll have a clear idea of common challenges your customers face — and exactly which of your products you can try to cross-sell or upsell as a possible solution.
4. Practice active listening.
You might be able to cross-sell or upsell to your customers on the fly during a phone call or over an email exchange — so make sure to hone in on your active listening and reading skills for signals your customer might be ready to hear your offer.
If your customer wants expanded capabilities or is actively working to reach their goals faster, it might be the right time to mention how your other products or services can help get them there.
How to Encourage Your Team to Upsell and Cross-Sell
From a business perspective, it’s far easier to sell to existing customers than to bring on new ones. It usually means that your sales team doesn’t have to prospect, qualify, or build a relationship. Your customer success team likely knows them too. And your business already has trust and credibility with the customer.
Expanding your account means clients are less likely to churn. The more products and services they invest in, the more difficult it will be for them to switch vendors or develop an in-house solution.
But in the hectic day-to-day, it can be tough for sales reps to get in touch with current customers. Long-time reps may be hesitant to make changes to a relationship that already works. Team members may not want to reach out to customers who are waiting for a new feature or bug fix that’s delayed.
And conversations with current customers are different. They often need more personalized knowledge of a client’s needs, goals, and preferences.
To encourage your reps to cross-sell and upsell, use these four strategies.
1. Try semi-annual check-ins.
Every six months, your sales team should check with their customers. This gives them a chance to review their progress, gauge their satisfaction, and look for opportunities to expand the account.
It’s a good idea to foreshadow these calls before the deal is even won. For example, during the sales presentation, a rep might say, “Besides [X resources] we have for our customers, I’ll meet with you twice a year. We’ll answer any questions you might have and make sure you’re getting as much value as possible from the product.”
Once it’s nearing the six-month mark, they should schedule a 30-minute call. Before the call, they should review any customer service notes or outstanding help tickets.
After a rep has met any new stakeholders, they should help the customer with any problems they may be facing. Then, using knowledge of their situation and history with the company, they can introduce an upsell or cross-sell.
For example, they could say, “In the past six months, you’ve increased your order quantity of [X material] by 20%. It would be cost-effective to buy [Y material] at the same time. By purchasing it from us rather than another supplier, you’ll save [Y amount] on every shipment.”
2. Eliminate fear of checking in.
Some salespeople don’t like calling current customers. They don’t want to engage if the product hasn’t lived up to their customer’s expectations.
But your team is a great resource to offer insights to clients if the product isn’t performing how they’d like.
If you notice a rep who seems hesitant to check in, ask what they think will happen. You may need to probe a little, but they’ll usually end up saying they’re afraid of the customer canceling. Tell them that’s highly unlikely — and that these are the three common outcomes:
- The customer adores the product. This gives your rep the perfect opportunity to offer an upsell or cross-sell.
- The customer is fine with the product. In this case, your rep can help them work out any issues they’re experiencing. They might also appreciate an upsell or cross-sell that can solve a new problem.
- The customer is unhappy. In this case, the rep can develop a plan to help them and hopefully rekindle the relationship.
Sales teams can also connect with customer success managers (CSMs). CSMs can cross-sell and upsell when they spot an opportunity further down the line with a customer once they’ve already purchased the initial product.
Throughout email exchanges or phone conversations, customers might mention an interest in expanding into a different vertical or wanting more capabilities with the product they’re using — which can signal that they’re ready to hear about other options.
3. Educate your team and customers.
Your team can’t sell new products or services if they don’t understand them.
Every time your company launches a new feature, hold product training sessions. If your company makes constant product updates, you may want to schedule quarterly or monthly sessions.
Besides your sales team, it’s also a good idea to include support, marketing, and operations teams in these training sessions.
These sessions should cover:
- Product functionality
- Use cases
- Potential ROI
- How to position the product
- Which types of customers or prospects it’s best for
You may also want to record these demos so your reps can share them with current customers.
4. Remember to continually add value.
Your team should add value for your customers with every interaction.
For example, your sales team might set a Google alert for client brand names. This way they know every time a client company gets mentioned in the news. Then they can connect to offer value on the update, like sharing a local contact after a client moves to a new office.
Gestures like this show customers your team cares. Then, when the time comes for upselling or cross-selling, they’ll be more than willing to engage.
You can promote this behavior in three ways:
Bring current customers to team-wide meetings.
This lets customers share their experiences. This will help your team better understand your customers. It will also show them the impact of adding value after the sale.
Offer a library of resources.
Develop blog posts, ebooks, videos, case studies, and more on a variety of topics relevant to customers. Then, encourage your team to share this content when communicating with their clients.
Track progress with every team member.
When you talk to your team, check in on their upselling and cross-selling performance. This will keep these goals top-of-mind for your team. You’ll see the difference in your results.
16 Everyday Examples of Upselling and Cross-Selling
B2B Sales Team
Upselling
- A sales representative lets customers know in advance about an upcoming price increase, then explains upgrade options at a similar price point. This is often a useful end-of-month or end-of-quarter discount.
- The sales team offers priority access to new or updated features. This is a typical upsell for SaaS companies.
Cross-Selling
- A sales rep lets the customer know that they can add a video editing tool to their current photo editing subscription.
- The sales team offers a bundle of grouped products, services, and features at a discounted rate.
HubSpot Research says that bundling is the most popular strategy for cross-selling. 63% of surveyed sales teams offer bundles.
Customer Success Team
Upselling
- Customer success teams can use client data to recommend useful upsells to customers. For example, say your writing tool charges users by the number of words. You can let a customer know when they are getting close to their limit and recommend upsell options that can also improve the user experience.
- A customer service team offers detailed product walkthroughs. During these product tours, service teams can show customers both basic and advanced product features.
Cross-Selling
- Customer service team solves customer problems by introducing product add-ons during an online chat.
Customer Education
Upselling
- A company adds feature page links to knowledge base articles. Some SaaS product questions have simple answers, but they also require an upgrade. This option informs customers and makes the solution easy to find and put in place.
Cross-Selling
- A business adds extra products that add value to the main product and help pages. For example, say your company sells desks. Your product photos, descriptions, instructions, and text can also include desk accessories that add value.
- A software company offers add-on service options with purchases, like advanced or long-term support and training.
Online Store
Upselling
- An online store selling hard drives offers three different memory sizes with pricing. A graphic highlights the most popular of the three options.
- An online beauty store offers a subscription option for mascara, with a discounted price for monthly delivery.
Cross-Selling
- A customer looks at t-shirts in an online store. They have the option to add a sweatshirt to their order for a discount on both items.
- An online store for cameras adds a popup at time of purchase for an added warranty to protect the new camera.
- A mattress store online adds a featured products gallery at the bottom of the product page. This gallery includes products like pillows, sheets, and duvet covers a customer might add to their purchase.
In-Store Sales Team
Upselling
- A customer goes shopping for a standard alarm clock. At the store, the salesperson suggests an alarm clock that also shares the daily weather forecast.
- A shopper is looking for a picture frame. They share that the frame is for an anniversary present with the salesperson. Based on this information, the salesperson shows the shopper some special occasion frames at a higher price point.
Cross-Selling
- A customer buys a new jumpsuit, but the waist is a bit looser than they’d like. As they check out at the register, a salesperson lets them know about the store’s alteration service that can take in the jumpsuit for a small extra fee.
Landing Page
Upselling
- A business owner is looking for project management software and the pricing page shows three plans. Each plan shows what features the plan includes. This shows the owner the added value of the more expensive plans and what they would miss if they chose the free plan.
- A landing page includes a testimonial about the highest tier plan. Because the testimonial solves an important problem for the user, it convinces them to upgrade.
Cross-Selling
- A camping online store adds a landing page of frequently forgotten camping gear to their buyer journey. This page helps customers add easy-to-forget items to their cart before checking out.
Online Service
Upselling
- An online yoga instructor offers weekly and monthly class passes, offering a discount for monthly signups.
- A SaaS business offers access to higher plan features during a free trial, then offers a discount to upgrade after the trial ends.
- An online purse rental service offers access to premium handbags for a slight price increase.
Cross-Selling
- An online language tutor offers to add SAT and ACT training at a discount.
- A vacation house rental service offers local tours and amusement park passes at a discount at the time of reservation.
Email Marketing
Upselling
- A business marketer uses a free tool to build an app. Then they get an email from the app with other tools to buy that might be helpful after building an app.
- A customer completes a task in an online tool, and it prompts an email that offers a discount for advanced features.
Cross-Selling
- A purchase confirmation email for hair ties includes an image gallery of hair styling products to buy next.
Bolster your sales with upselling and cross-selling.
Cross-selling and upselling aren’t always straightforward. Doing this tactic right takes optimal timing, keen awareness, and empathy.
If you can keep a pulse on how your customer is feeling, have an idea of the features or products they stand to gain the most from, and know when they’ll be most receptive to an additional offer, you’ll be able to upsell and cross-sell with the best of them.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in October 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

